-
C-F -- move right one character, same as right-arrow
C-B -- move left one character, same as left-arrow
C-N -- move down one line, same as down-arrow
C-F -- move up one line, same as up-arrow
-
C-E -- move cursor to the end of the line
C-A -- move cursor to the beginning of the line
-
C-V -- page down, same as page-down key
Alt-V -- page up, same as page-up key
ESC-< -- move to the beginning of the file
ESC-> -- move to the end of the file
-
C-D -- delete, same as Delete key
C-K -- Delete text to right of the cursor and place it in a Kill Buffer
C-Y -- Places contents of Kill Buffer to the right of the cursor -- "Yank" the kill buffer
C-@ -- Set Mark -- moving up or down will highlight the file -- much like Shift-Up-Arrow or Shift-Down-Arrow
Keyboard Macros
-
C-X( -- Start Recording Key Strokes
C-X) -- End Recording Key Strokes -- Keyboard Macro Now Defined
C-Xe -- Execute Keyboard Macro
C-X Alt-N -- Name Keyboard Macro -- (name-Kbd-Macro)
C-F3 -- Write the State File -- Epsilon.Sta -- Saves Keyboard Macro as Epsilon Command
Alt-X(name of Keyboard Macro) -- executes named Keyboard Macro
C-UAlt-X(name of Keyboard Macro) -- executes named Keyboard Macro 4 Times


Complete List of Epsilon Commands that can be use in Text Macros
-
Bring All three Files up in Epsilon so
that all three are in buffers.
Set up a Split Window and place KEITH.DAT in the top window and ELEC2000.DAT in the bottom window. It should look like this:
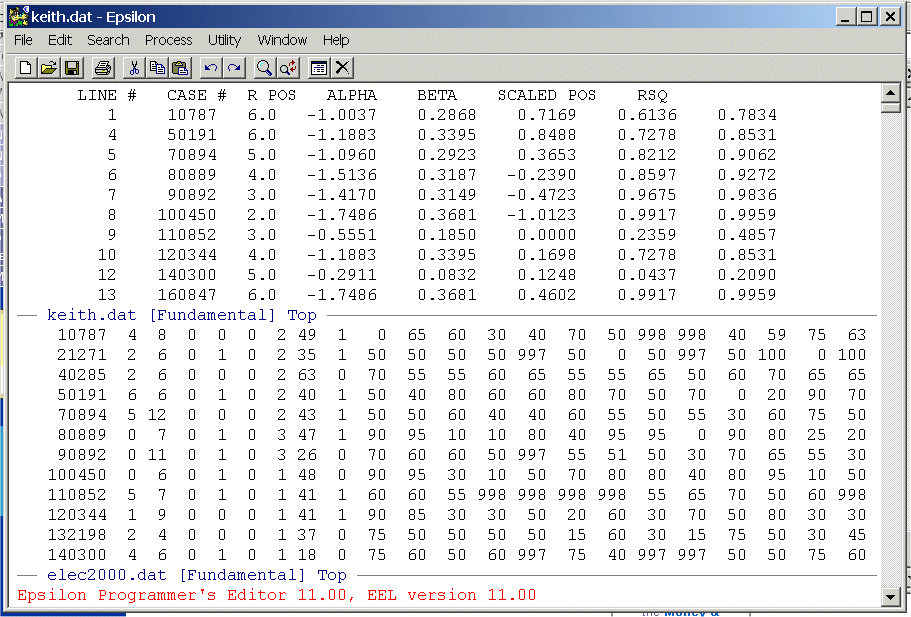
Set the cursor in the bottom window at the beginning of the first line and then set the cursor in the top window at the beginning of the second line. When the macro is invoked it expects the cursor to be in the top window. When the macro moves into the bottom window the first time it expects to be at the top of the file. Note that the macro is using the "CASE #" of the top file to to match the corresponding row of the bottom file. The two files have different numbers of lines but all the "CASE #"s of the top file are in the bottom file. The macro uses this to search down the bottom file to find the correct row.
Type ALT-X and then type load-buffer and you should see:
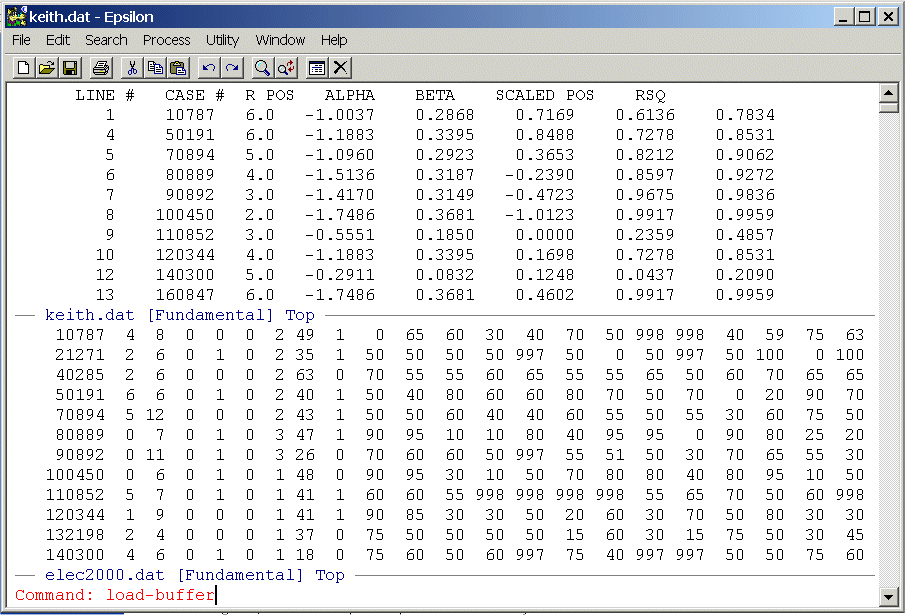
Now hit Enter and you should see:
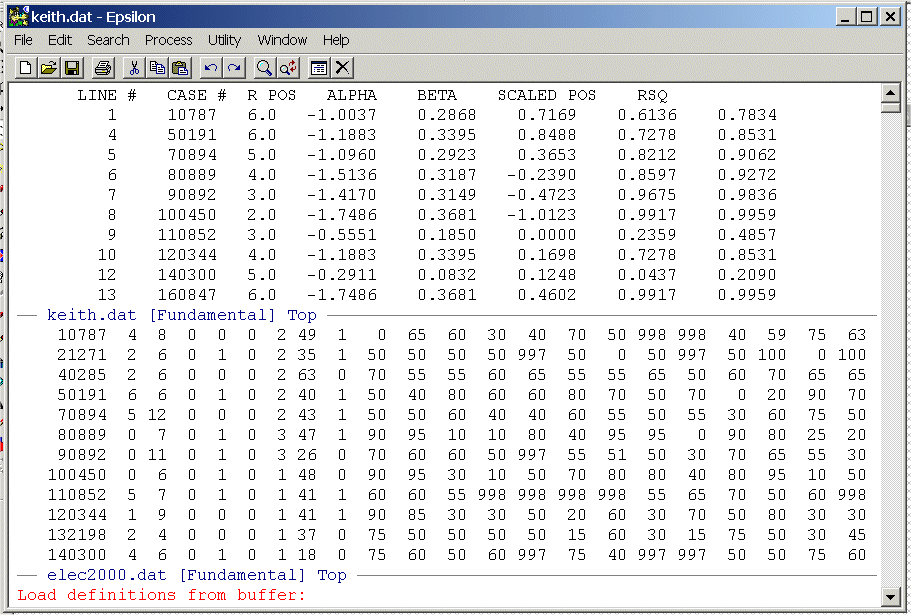
Now type Macro_hw6a.txt and hit Enter and you should see:
The 0 errors detected means that Epsilon accepted your Macro.
To execute the macro one time type ALT-X and then type the name of the macro (this is not necessarily the name of the file containing the macro!). In this case the name of the macro is hw-test. You should see:
Now hit Enter and you should see:
Note that the cursor is now at the third line in the top window and the party ID code "4" from the first line of the bottom window is inserted into the coordinate file.
To run the macro 5 times type: C-U and then 5 and you should see:
Now type Alt-X and then hw-test and you should see:
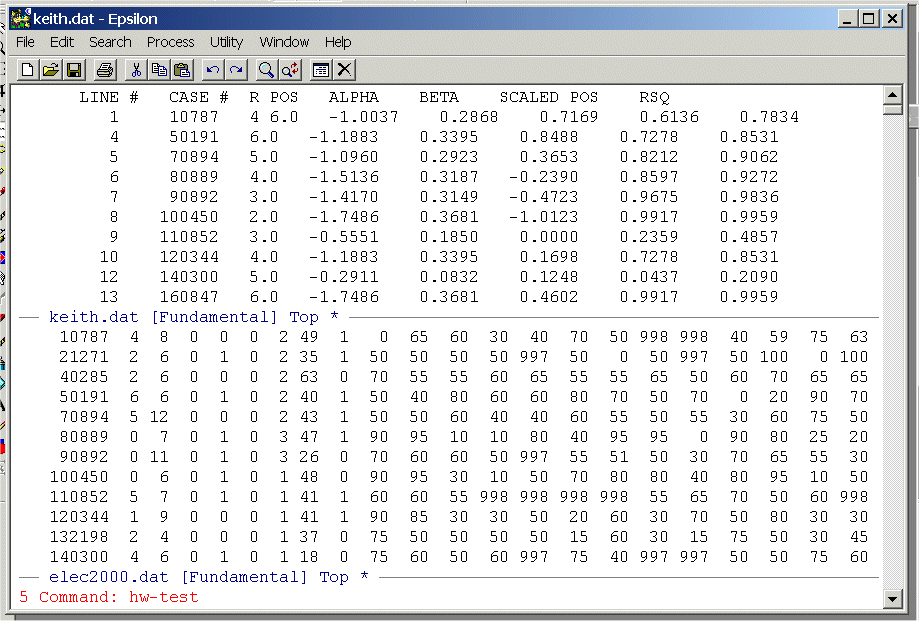
Now hit Enter and you should see:
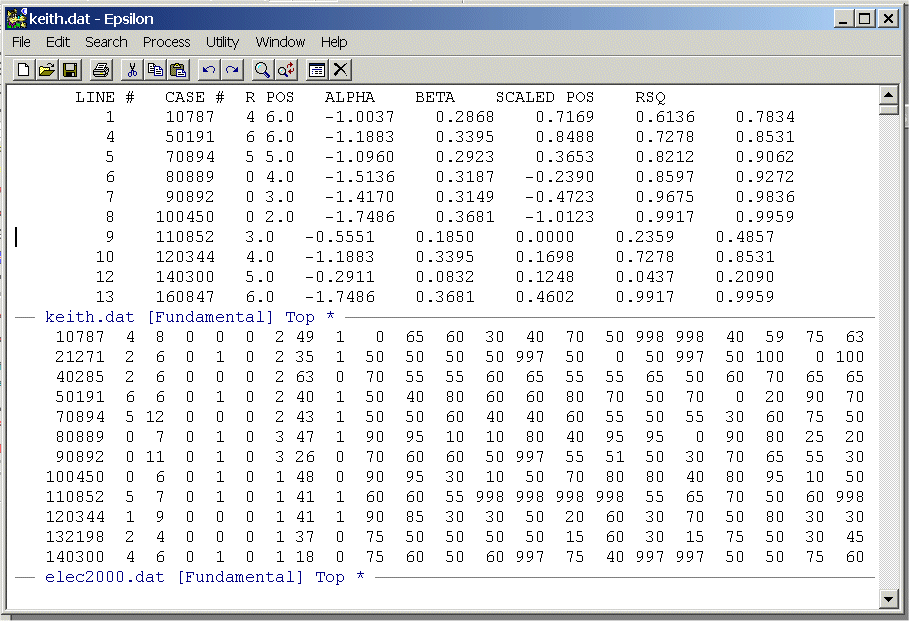
You can run the macro as many times as you want by using the C-U command as shown in step (j) above.
-
Bring All three Files up in Epsilon so
that all three are in buffers. Your screen should look like this:
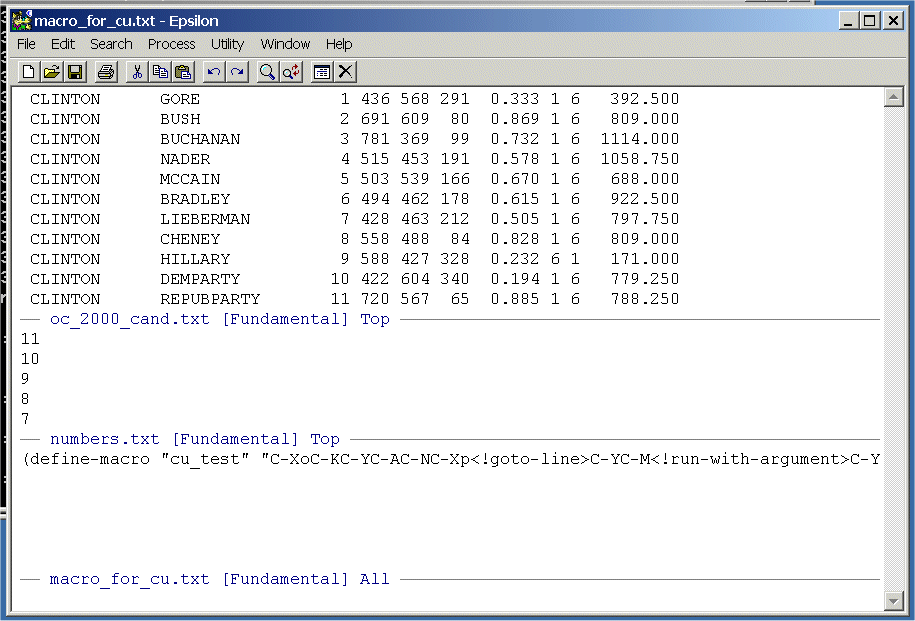
Set the cursor in the bottom window at the beginning of the first line and then set the cursor in the top window at the beginning of the second line. When the macro is invoked it expects the cursor to be in the top window. When the macro moves into the bottom window the first time it expects to be at the top of the file. The macro picks up an integer from the numbers.txt file and then goes back up to the OC_2000_Cand.txt file. It then goes to the line corresponding to the integer picked up from OC_2000_Cand.txt and then the macro uses the run-with-argment feature. The integer picked up is 11 so that the effect is C-U11C-F -- move the cursor to the right 11 spaces. The macro then simply places the remainer of the line in the kill buffer and moves to the beginning of the next line.
Type ALT-X and then type load-buffer and then type ALT-X and then cu_test and you should see:
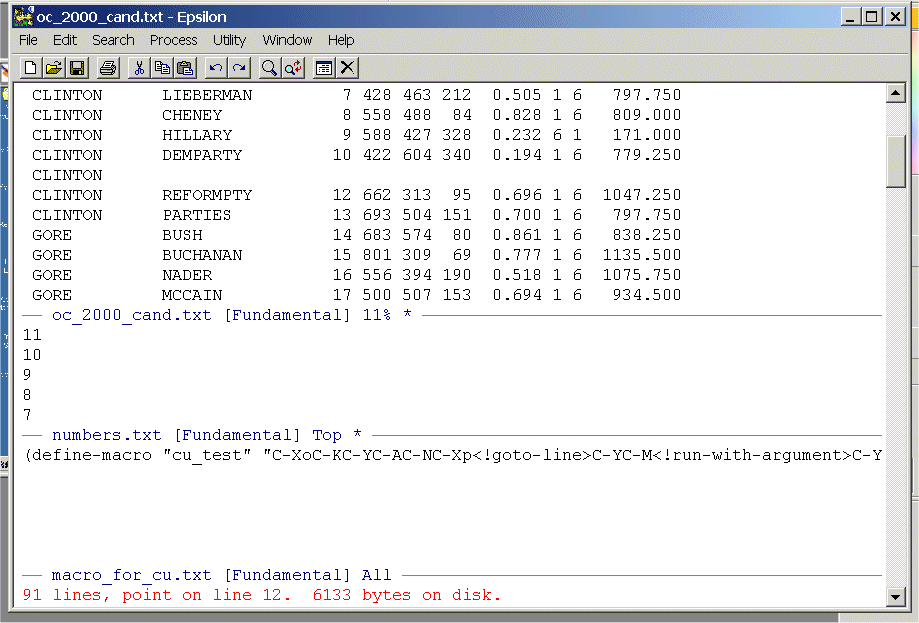
This macro picks up the digits 1, 2, 3, ... , 1209 from the file names in the middle window, then moves to the lower window and opens the entire directory with C-XC-F, it then toggles down to the corresponding file using run-with-argument and C-N, opens the file, does a search and replace within the file, saves the file, and then moves back to the middle window.
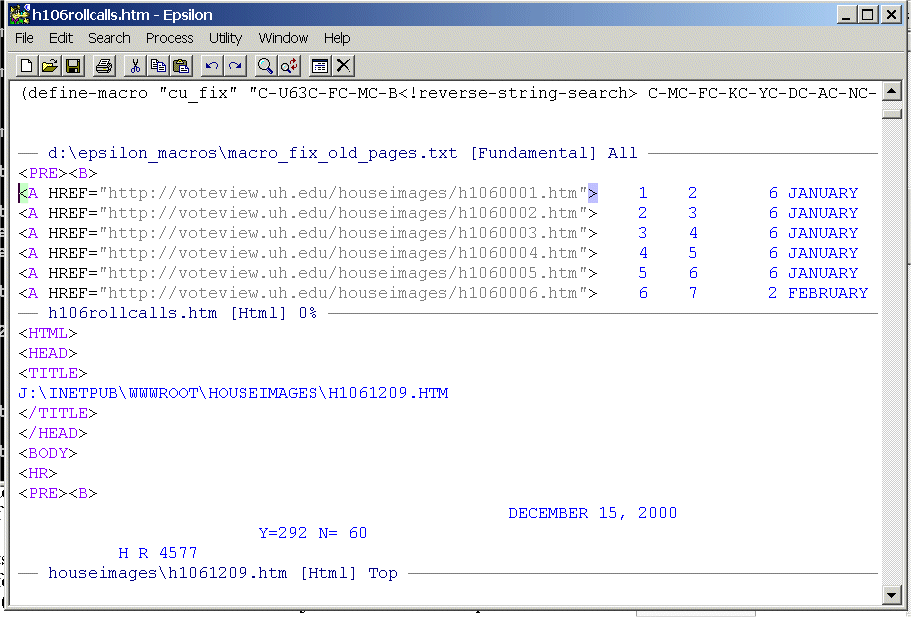
This macro begins in the top window, picks up the file name in the middle window, moves to the lower window and searches the directory for the file name using string-search, opens the file, copies a block of text within the file, re-opens the directory tree (C-XC-F), moves to the upper window, and yanks the copied text.
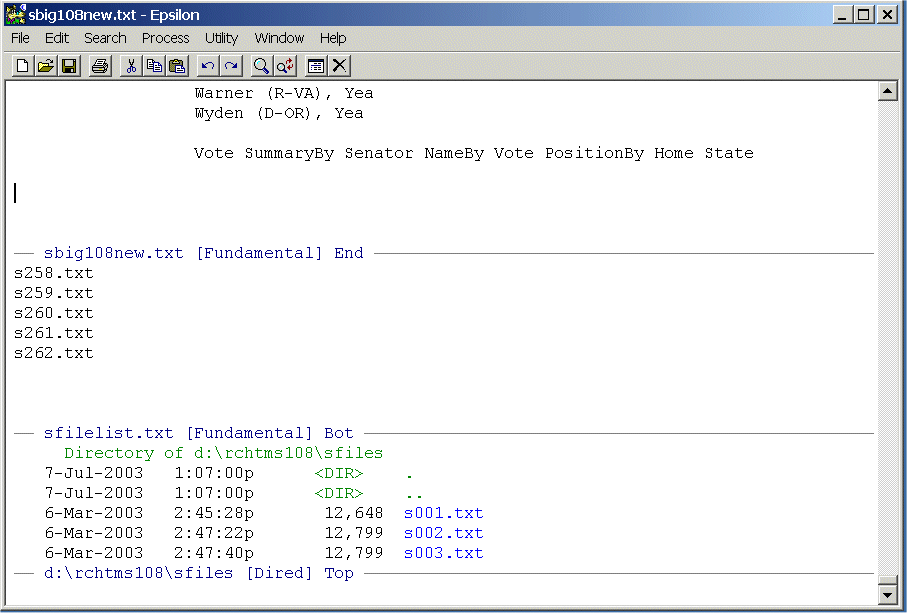
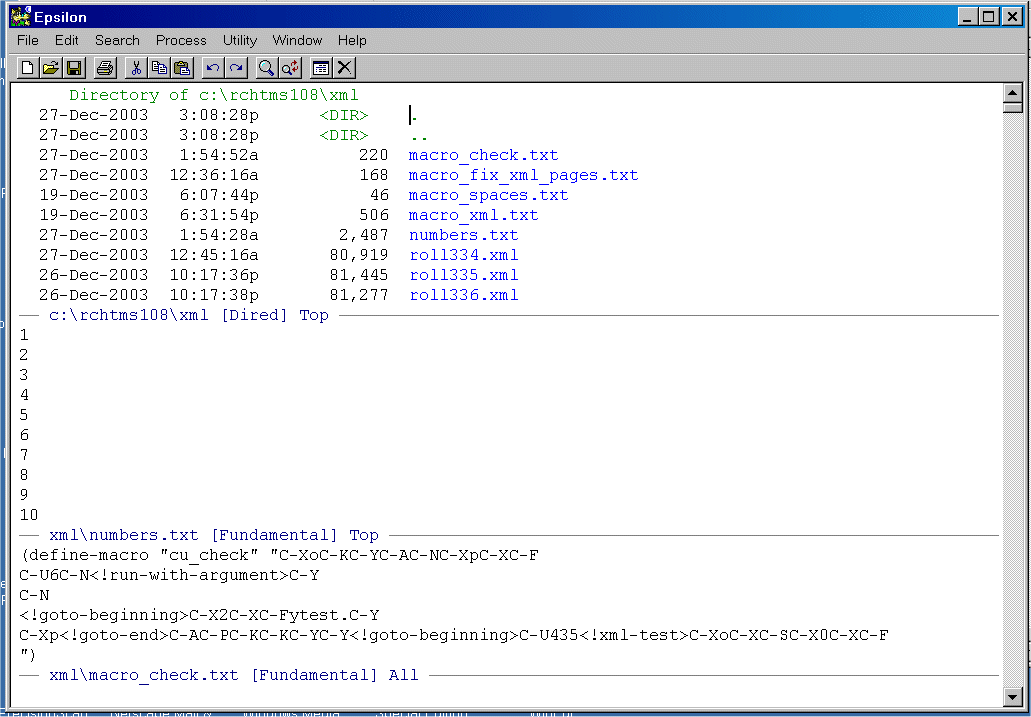
This macro begins in the top window showing the directory containing the XML files, picks up a number from the Numbers.Txt file, goes back to the top window and uses the number to move down the directory listing and then open a file. Once the file is open it splits the window and then writes a dummy file YTEST.[number], and then returns to the XML file and executes the Macro_Xml.txt that processes the XML file into the lower window. When it finishes, it closes the YTEST.[number] window and then opens the directory edit window.
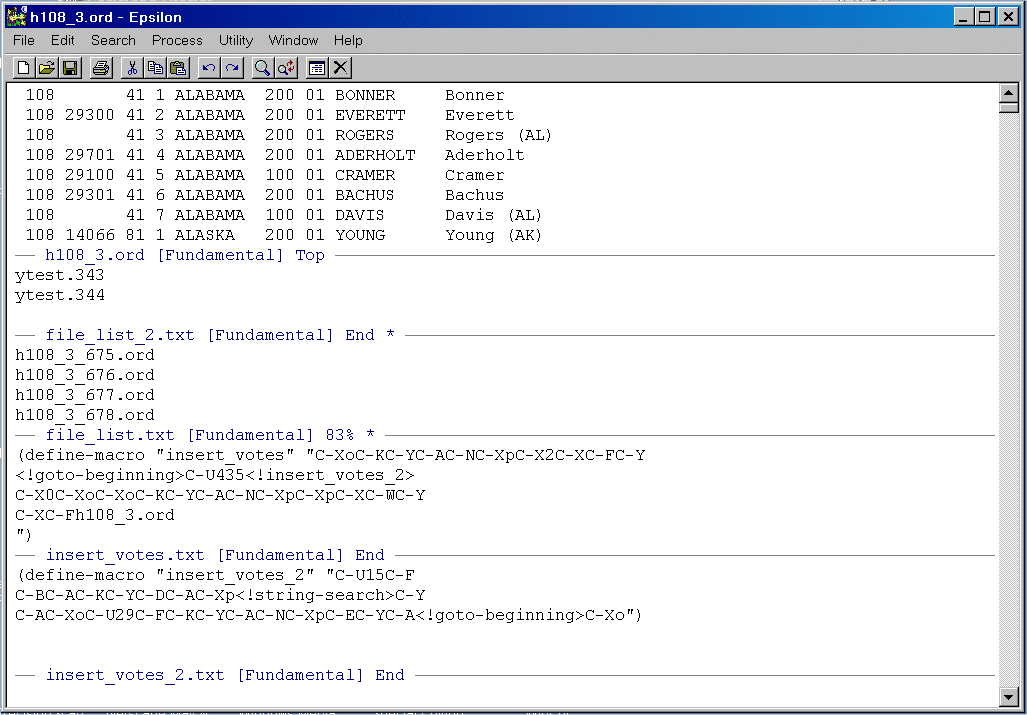
This macro begins in the top window showing H108_3.ORD -- template for roll call file -- goes down one screen to pick up a file name from the File_List_2.TXT file, returns to the top screen, splits the window, and opens the file from File_List_2.TXT in the new window. It then takes the votes from the YLIST.[] file and places them in the H108_3.ORD file. When it is done, it closes the window with YLIST.[], goes down two windows to FILE_LIST.TXT, picks up a file name, goes to the top window and saves the H108_3.ORD file as H108_3_[N].ORD.